Sub-Assistants and Orchestration
Create orchestrator assistants that coordinate multiple specialized assistants to handle complex, multi-faceted tasks. This hierarchical approach enables effective agent-to-agent communication and task delegation.
Overview
The multi-assistant capability allows you to build an orchestrator assistant that utilizes other assistants as tools. The orchestrator intelligently delegates specific tasks to specialized sub-assistants based on the request context.
Key Concepts
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Orchestrator Assistant | Primary assistant that coordinates and delegates tasks to sub-assistants |
| Sub-assistants | Specialized assistants added as tools to the orchestrator |
| Hierarchical Processing | Complex tasks broken down and distributed to appropriate specialists |
| Context Sharing | Sub-assistants access chat history to build on previous interactions |
Configure an Orchestrator
Create the Orchestrator
-
Navigate to Assistants → Project Assistants.
-
Click + Create Assistant.
-
Fill in basic properties:
- Name: Descriptive name for the orchestrator
- Description: Explain the orchestrator's coordination role
- System Instructions: Detailed instructions on when to use each sub-assistant
Add Sub-assistants
-
Scroll down to the Tools section.
-
Locate the Sub-assistant field with dropdown menu.
-
Use the search function to find assistants to add as sub-assistants:
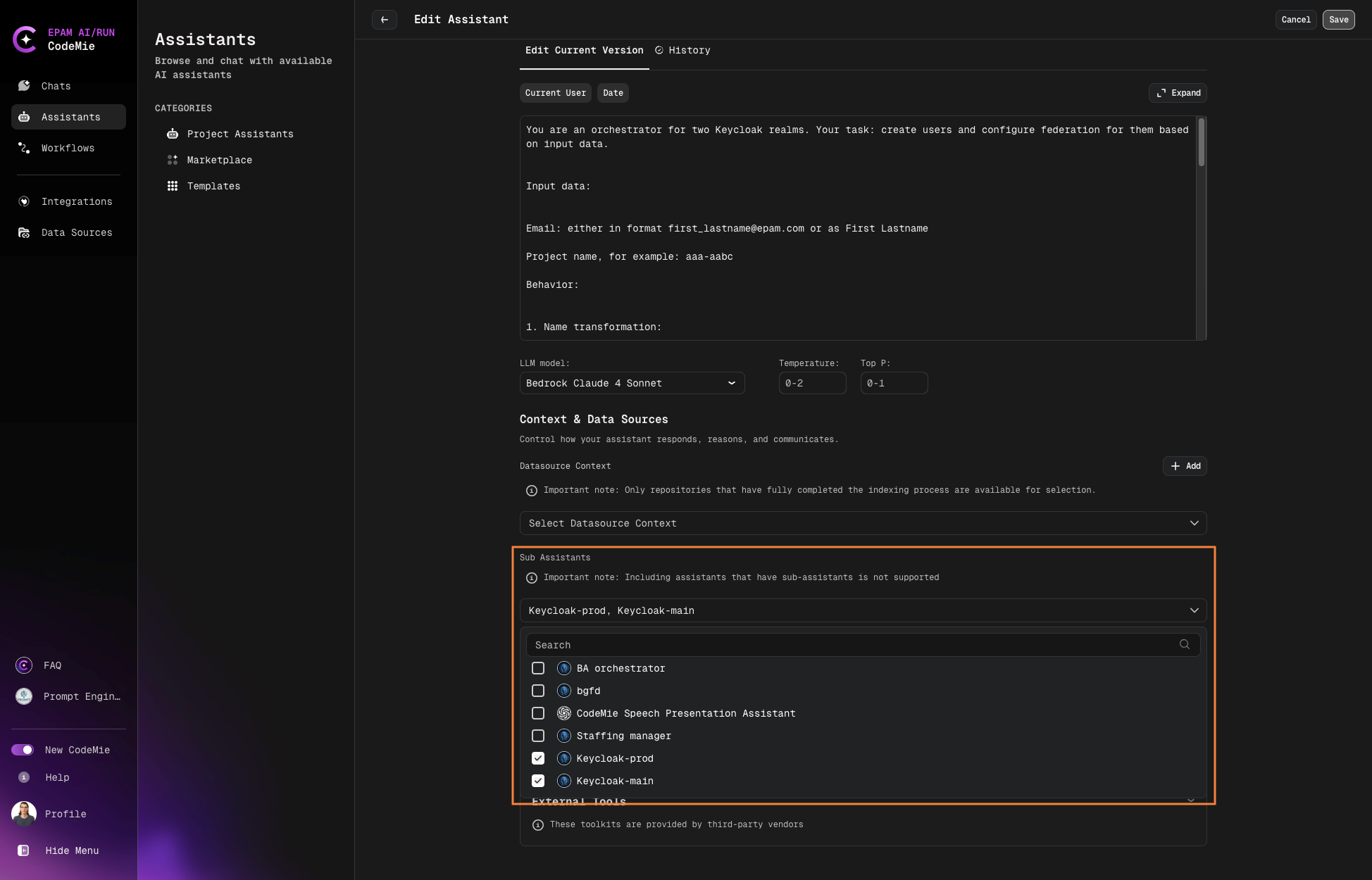
- Only assistants within the same project can be added
- Cannot select assistants that already have sub-assistants (no nesting)
- Cannot select the assistant itself as a sub-assistant
Configuration Best Practices
1. System Instructions
The orchestrator requires detailed instructions to determine which sub-assistant to use for each task:
- Describe each sub-assistant's capabilities and specialization
- Define clear criteria for when to delegate to specific sub-assistants
- Include examples of request types that match each sub-assistant
2. Sub-assistant Descriptions
Each sub-assistant needs a clear description explaining:
- Its purpose and specialized capabilities
- Types of tasks it handles best
- Any limitations or constraints
3. Context Management
Sub-assistants can access chat history, enabling them to:
- Build upon previous interactions
- Maintain conversation continuity
- Reference earlier information without re-explanation
Example Use Case
Test Documentation Orchestrator
Create an orchestrator for test documentation and regression planning with three specialized sub-assistants:
| Sub-assistant | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Checklist Generator | Creates checklists based on user stories |
| Test Case Writer | Generates manual functional test cases |
| Regression Analyzer | Analyzes code changes and provides regression testing recommendations |
How it works:
- User requests test documentation help
- Orchestrator analyzes the request type
- Delegates to appropriate sub-assistant(s)
- Coordinates responses into coherent answer
View Configuration
To see which sub-assistants are configured:
- Open the orchestrator assistant details.
- Review the Sub-assistants section in the configuration panel.
- See the complete list of available sub-assistants and their descriptions.
Best Practices Summary
- Specialization: Create focused sub-assistants with clear, distinct capabilities
- Clear Instructions: Provide detailed orchestrator instructions defining delegation logic
- Descriptive Naming: Use names that clearly indicate each sub-assistant's purpose
- Testing: Test the orchestrator with various scenarios to verify proper delegation
- Documentation: Document each sub-assistant's role for team members
The key to successful orchestration is clear boundaries between sub-assistant responsibilities. Avoid overlapping capabilities that could confuse the orchestrator's delegation logic.